Quad - 4-Service Based Approach
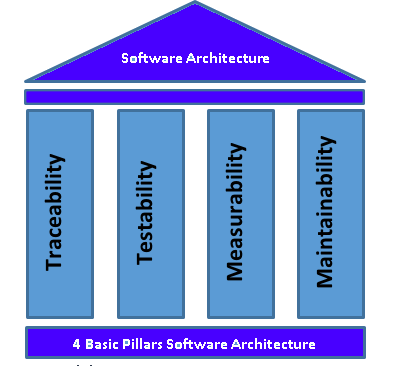
Traceability
There are two facets of traceability. Traceability entails the mapping of requirements to the final product. This traceability matrix allows all stake holders to define and confirm the definition of “Done”. A well-defined traceability matrix also supports the maintainability of the software product.
Read moreTestability
A TDD (Test Driven Development) appraoch is followed to ensure that automated tests are in place to test critical source code components. These tests are the foundation of a software architecture. Althougn exploratory testing has its place, it is time-consuming, expensive and does not support regression effectively. TDD, although time-consuming to setup and apply consistantly, pays big dividents later in the product development phases and especailly during post implementation maintenance and enhacements.
Measurability
In order to determine success, failure and to be able to quantify in measurable terms the level of success is vital. In order to achieve this goal, requirements are translated in QA test cases that form the foundation for measurement, the measurability matrix. As mentioned before, this is part of the definition of "Done". The measurability matrix typically includes other matrices like performance and load-test, error handling and logging.
Maintainability
Software Maintainability: 75% of Your Budget Is Dedicated to Software Maintenance.
Software maintainability is defined as the degree to which an application is understood, repaired, or enhanced. Software maintainability is important because it is approximately 75% of the cost related to a project!
Software Architecure
The roof of the four pillar architecture is the software architecture. This is mostly abstract but a vital component to define the framework for the implementation of the four pillars. It defines the aspects of the framework like resources availability, technology stack, interfaces, APIs, etc.
Testimony
“Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”
“Design is not just what it looks like and feels like. Design is how it works.”

